The diagnosis – as quickly as possible
Every diabetes patient must undergo regular ophthalmological examinations. Even when the results are normal: frequent check-ups by the ophthalmologist are essential. This is because retinopathy can only be treated promptly when it is detected early. Important: Well-managed blood glucose and blood pressure could help avoid disease progression.
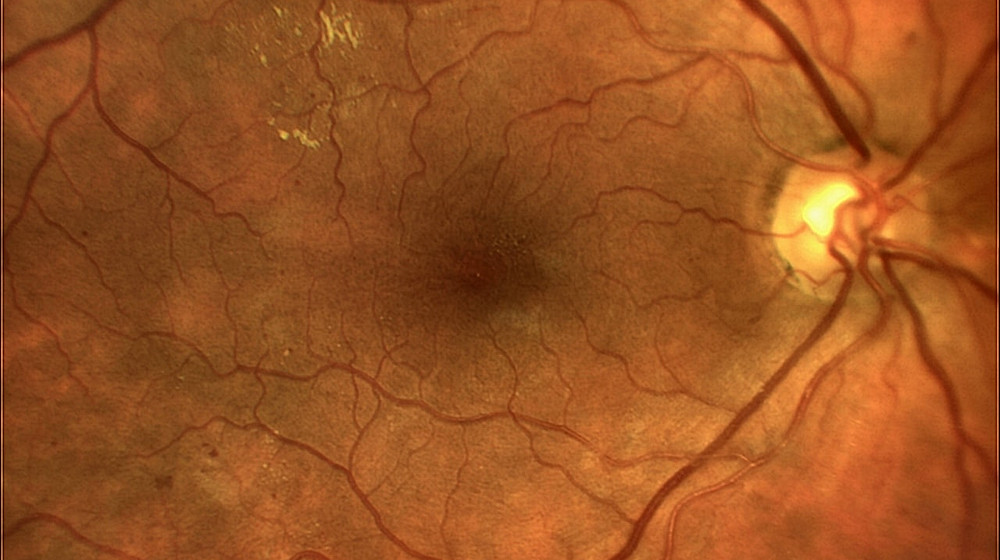
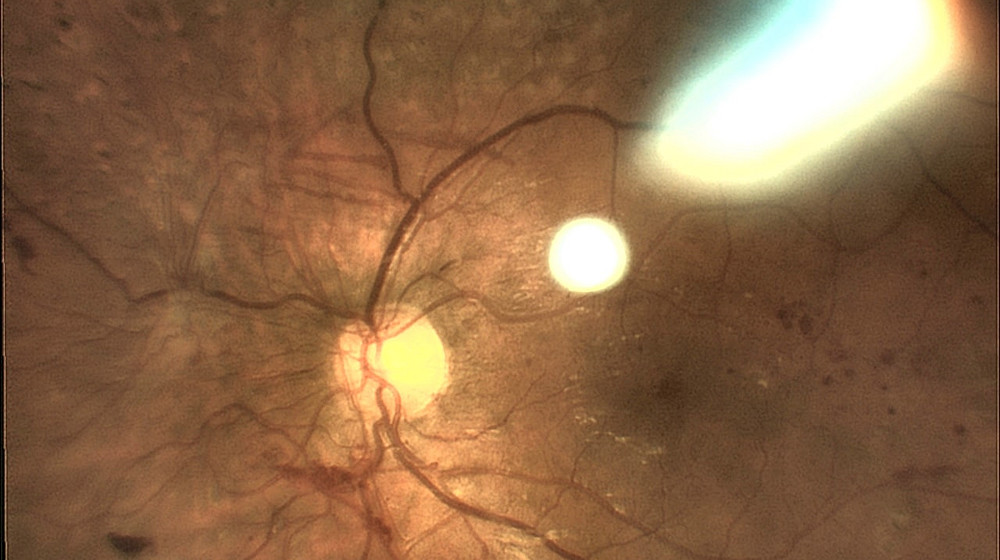
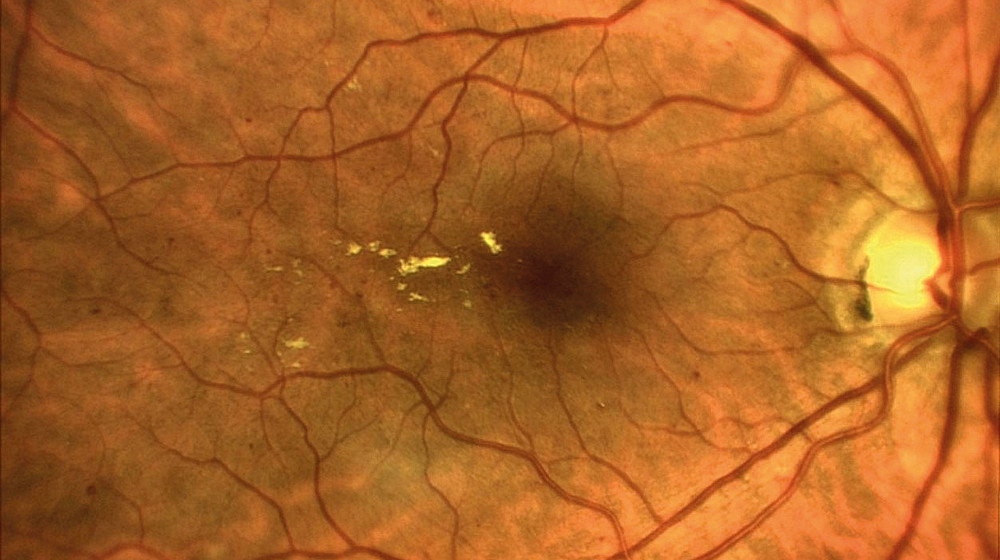
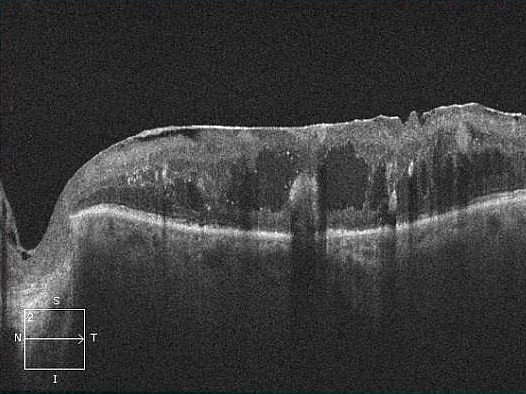
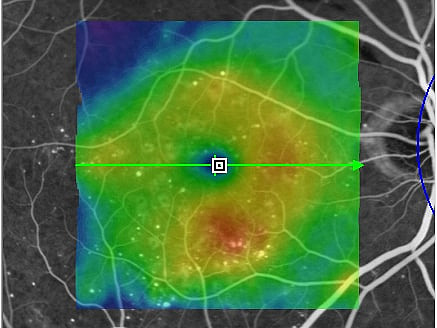
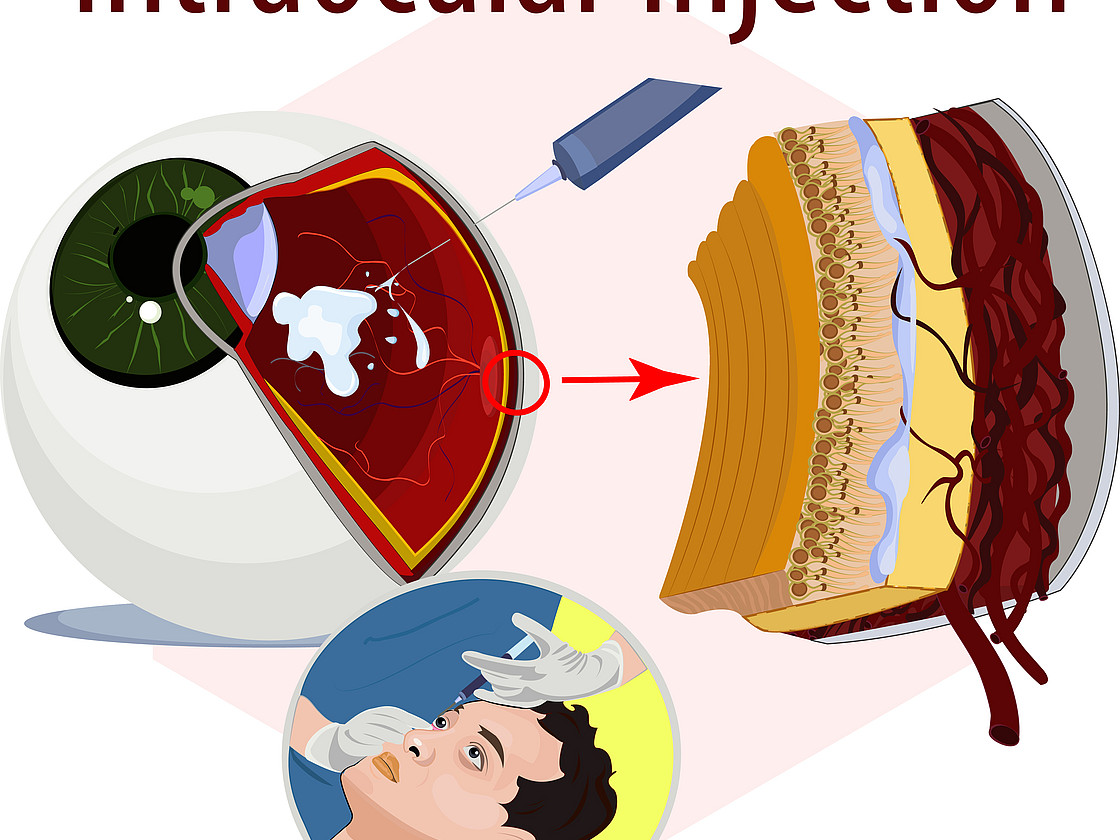
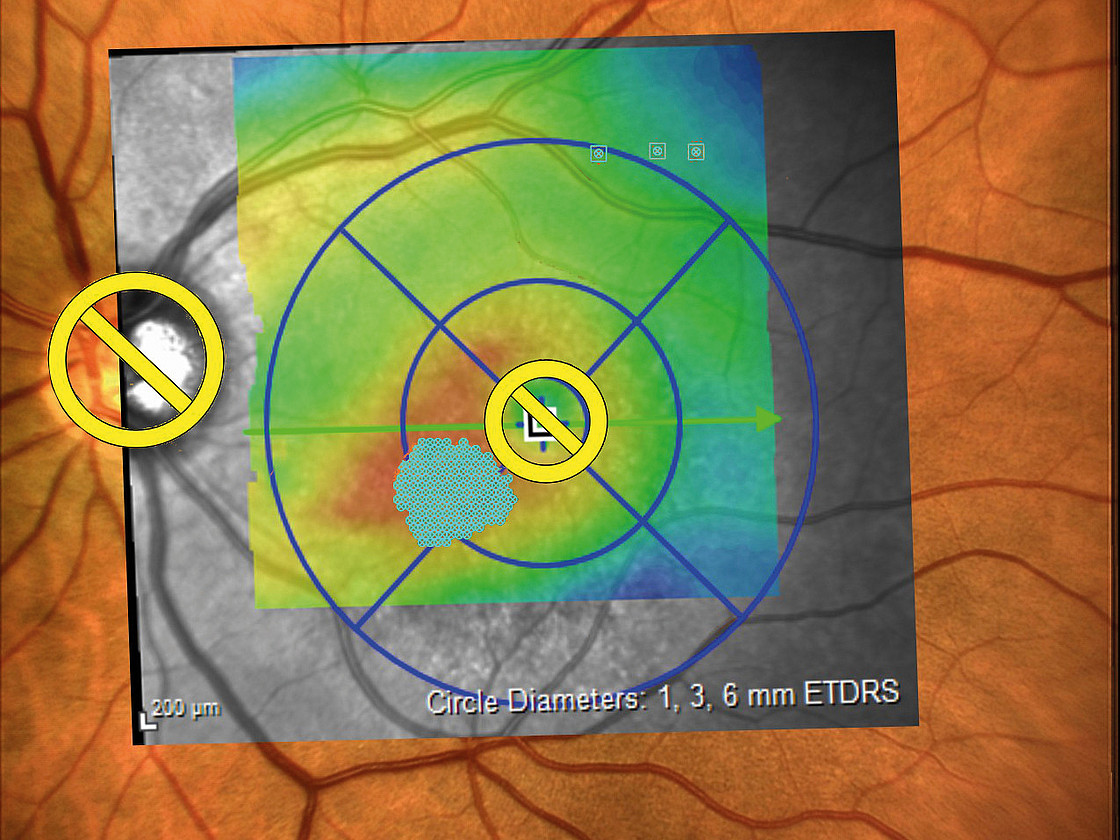
The examination: Changes to the retina are visible on the slit lamp. If these are present, this is followed by further diagnostic steps. One of these is fluorescein angiography. In this test, a dye is injected via a vein in the arm, which allows the vessels in the eye to be seen. Several photos are taken during the examination. These are used to assess whether and where the laser has to be used. "Optical coherence tomography" (OCT) is then used for a more precise examination. It depicts the individual layers of the retina and allows a number of changes to be detected. This makes it possible to determine the stage of diabetic retinopathy more accurately. It is thus easier for the doctor to define a treatment strategy for the patient.